KevinDailyStory.com – This article will discuss the ear anatomy, including the Tensor Tympani muscle. This muscle originates from the auditory tube and inserts onto the manubrium of the ear drum. It is innervated by the mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve and the trigeminal ganglion. Hence, it is also known as the stapedius.
The outer ear is composed of cartilage
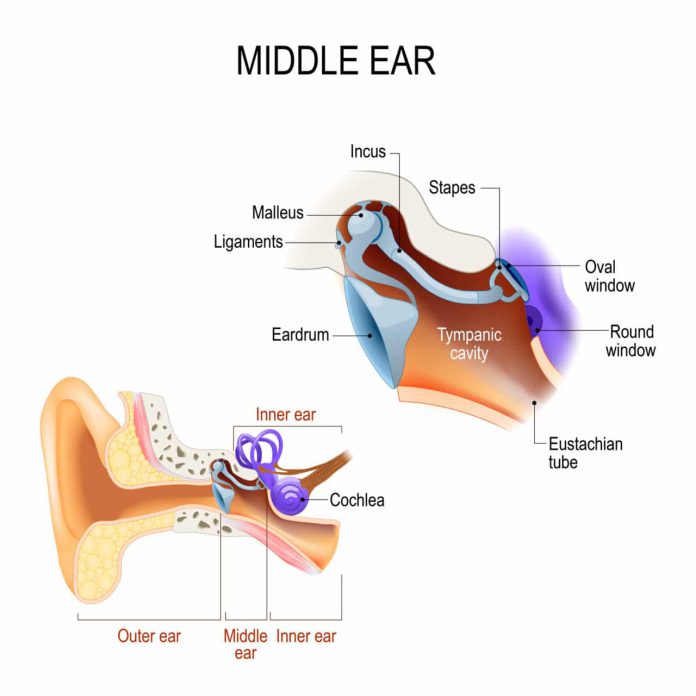
The ear is made up of three parts: the external acoustic meatus, the middle ear (the stapes, malleus, and incus), and the inner ear (labyrinth). The external auricle is composed of cartilage and serves to collect sound, which then travels to the middle otolith. However, the asymmetric shape of the external auricle introduces delays in the sound path. In addition, the occipital artery contributes to arterial supply to the auricle. Both named arteries are innervated.
The Tensor Tympani muscle is located in the bony canal above the auditory tube. It inserts onto the malleus bone, which helps in dampening loud sounds. However, it cannot protect the ear against sudden, loud noises. Its role is to absorb the sound and prevent it from damaging the inner ear. Hence, it is important to learn more about the Tensor Tympani muscle before undergoing surgery.
Tensor Tympani tendon is the most important part of the ear
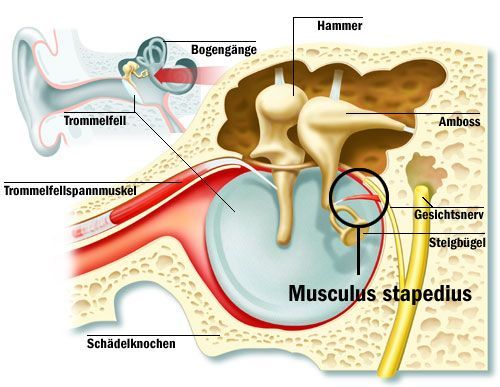
The Tensor Tympani tendon originates from the cochleariform process of the malleus. It attaches to the underside of the malleus neck. Aside from that, one specimen of the temporal bone was missing the stapedius tendon, but the rest were found to have it. Therefore, the Tensor Tympani tendon is the most important part of the ear.
The Tensor Tympani muscle is involved in the startle response to some sounds. A lower reflex threshold of the tensor tympani muscle contraction is known as tonic tympani syndrome. A person with a lowered reflex threshold of tympanic tensor tympani muscle contraction will have an elevated sensitivity to loud noises, resulting in ear pain, fluttering sound, and fullness.
The tympanic tendon must be trimmed if it has a contracture
The Tensor Tympani tendon can be identified with a 30deg or 0deg endoscope. The tensor tendon can then be severed with a blunt pick. Depending on the anatomy, this may require several passes. A blunt pick may also be used to deflect the tendon. In the meantime, a tympani tendon should be trimmed if it has a contracture.
The TM is made up of three separate functional units. The superior hemitympanum transmits lower frequencies and the inferior hemitympanum transmits mid-frequency sounds. The third unit, called the pars flaccida, is a receptive organ that receives sound waves. The TM is connected to the malleus through fibrous connections. If you’ve ever heard a ringing tone, you know how annoying it can be.
Referred sensory symptoms, such as the syndrome
This complex connects the ear to the brain, and the resulting problems are often caused by dysfunctions of this complex. These disorders may be caused by the Tensor Tympani muscle. These symptoms may be local, such as a fullness sensation in the ear. It could also be a referred sensory symptom, such as a burning mouth syndrome or a neuropathic complaint like palatal pain.
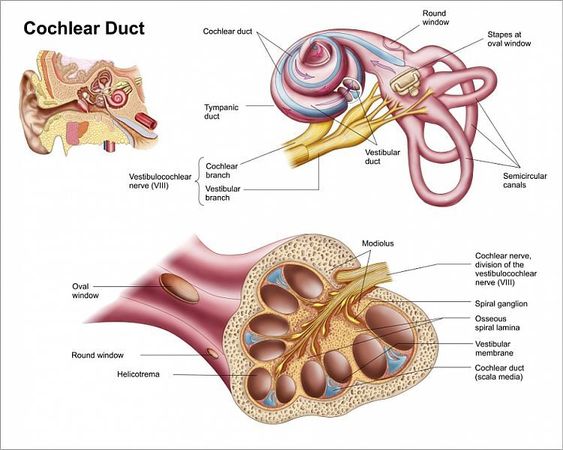
The otoacoustic emissions are a consequence of changes in the MOC neuron or MEM motor neurons. Otoacoustic emissions are sounds produced by the outer hair cells of the ear, which are electromotile. An ear mic is placed in the ear canal to record these sounds. These sounds serve as windows into the inner ear that are used to trigger reflexes.
The malleus, the largest earbone, is located in the epitympanic recess
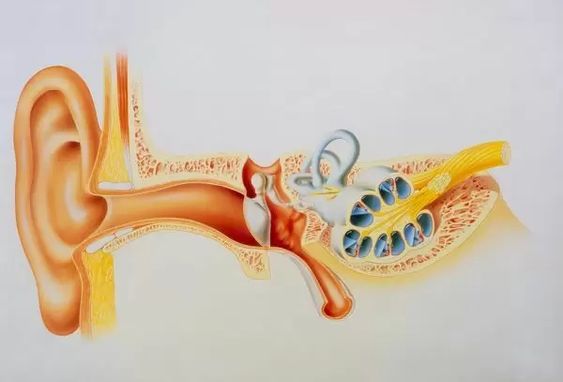
The ear is composed of three main components: the external ear, middle ear, and eustachian tube. The three bones connect to form a chain-like structure that transmits sound waves from the air to the inner ear. The auditory ossicles are attached to the tympanic membrane. The malleus, the largest ear bone, lies in the epitympanic recess. The malleus articulates with the next auditory ossicle.
The sensory trigeminal nerve innervates the dTCC and vTCC. The demarcation line runs through the pharynx and nasopharyngeal region and extends to the C2 spinal cord. The Vth nerve carries the TM. Activation of these muscles is a key factor in the symptoms of many disorders. However, the dTCC and vTCC have distinct functions.